White Patches on the Skin: Causes, Types, and Treatment Options
White patches on the skin can be concerning, but they are often harmless and treatable. These patches can result from various conditions, ranging from pigmentation disorders to infections. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and managing white patches on the skin.
Common Causes of White Patches
-
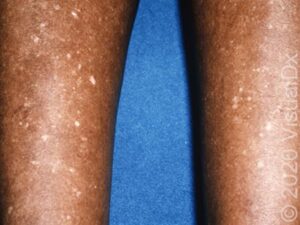
Vitiligo
- Description: An autoimmune condition where melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) are destroyed.
- Appearance: Smooth, white patches with well-defined borders.
- Common Areas: Face, hands, and body folds.
-
Pityriasis Alba
- Description: A mild form of eczema often seen in children.
- Appearance: Pale, scaly patches that may be slightly itchy.
- Common Areas: Face, arms, and upper trunk.
-
Tinea Versicolor
- Description: A fungal infection caused by Malassezia yeast.
- Appearance: Small, scaly patches that may be lighter or darker than surrounding skin.
- Common Areas: Chest, back, and shoulders.
-
Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation
- Description: Loss of pigment after skin inflammation or injury.
- Appearance: White patches where the skin has healed.
- Common Areas: Anywhere on the body.
-
Lichen Sclerosus
- Description: A rare skin condition that causes white, shiny patches.
- Appearance: Thin, wrinkled skin that may itch or tear easily.
- Common Areas: Genital and anal areas.
Diagnosis and Treatment
-
Diagnosis
- A dermatologist may perform a physical exam, use a Wood’s lamp, or take a skin biopsy to determine the cause.
-
Treatment Options
- Vitiligo: Topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, or depigmentation.
- Pityriasis Alba: Moisturizers and mild topical steroids.
- Tinea Versicolor: Antifungal creams or oral medications.
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Time and gentle skincare.
- Lichen Sclerosus: Topical steroids and regular monitoring.
Prevention and Care
- Protect skin from excessive sun exposure with SPF 30+.
- Maintain good hygiene to prevent fungal infections.
- Use gentle skincare products to avoid irritation.
- Consult a dermatologist for persistent or worsening patches.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- White patches spread rapidly or change in appearance.
- They are accompanied by pain, itching, or other symptoms.
- Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective.
Conclusion
White patches on the skin can stem from various causes, but most are manageable with proper care and treatment. Early diagnosis and a tailored approach are key to restoring skin health and confidence. If you’re concerned about white patches, consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance.
Pro Tip: Incorporate antioxidant-rich foods (e.g., berries, leafy greens) into your diet to support skin health and pigmentation.
